LLR contribution to reference frames and Earth orientation parameters
| Led by: | Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jürgen Müller |
| Team: | Dr.-Ing. Liliane Biskupek |
| Year: | 2019 |
| Funding: | Germany’s Excellence Strategy – EXC-2123 QuantumFrontiers (DFG), DLR-SI |
| Duration: | 2019 - 2025 |
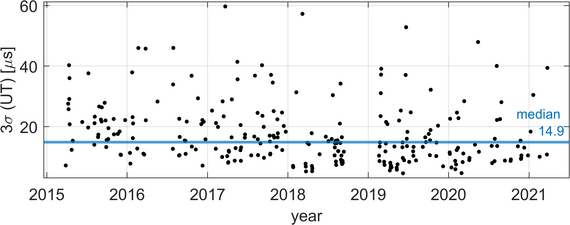
Since 2015, the number of accurate Lunar Laser Ranging (LLR) observations has greatly increased, mainly through measurements made with infrared laser light. These observations allow for better coverage of the Moon's orbit as well as better distributed measurements to the different reflectors. It also results in a larger number of observations being available per night. From the entire data set of LLR observations, the positions and velocities of the observatories on Earth can be calculated with an accuracy of a few centimetres and can be used into the realisation of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF). Due to the long-term stable lunar orbit, it is also possible to determine Earth's orientation parameters, such as the terrestrial pole coordinates or the Earth rotation.
In this project, the potential of LLR observations to contribute to station coordinates, velocities and Earth orientation parameters will be investigated. Furthermore, a combination with other geodetic space techniques (e.g. very long baseline interferometry, VLBI) is being prepared to enable a joint analysis of the respective measurement data.