Robot-based Calibration
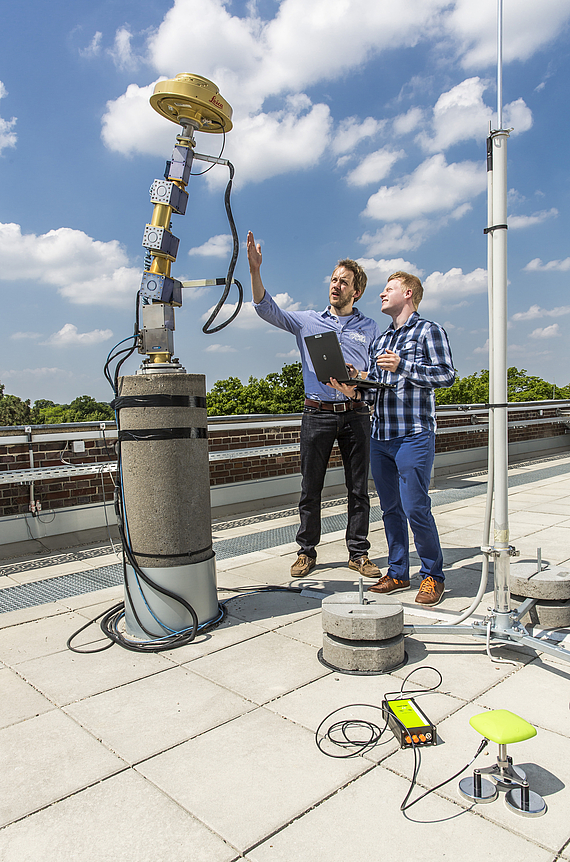
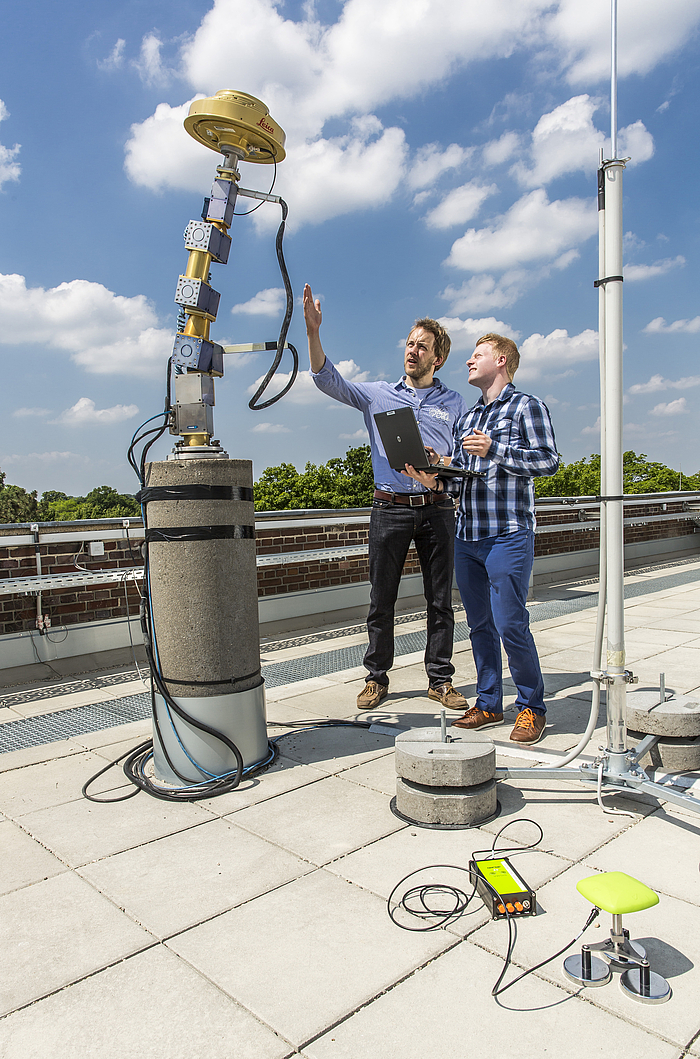
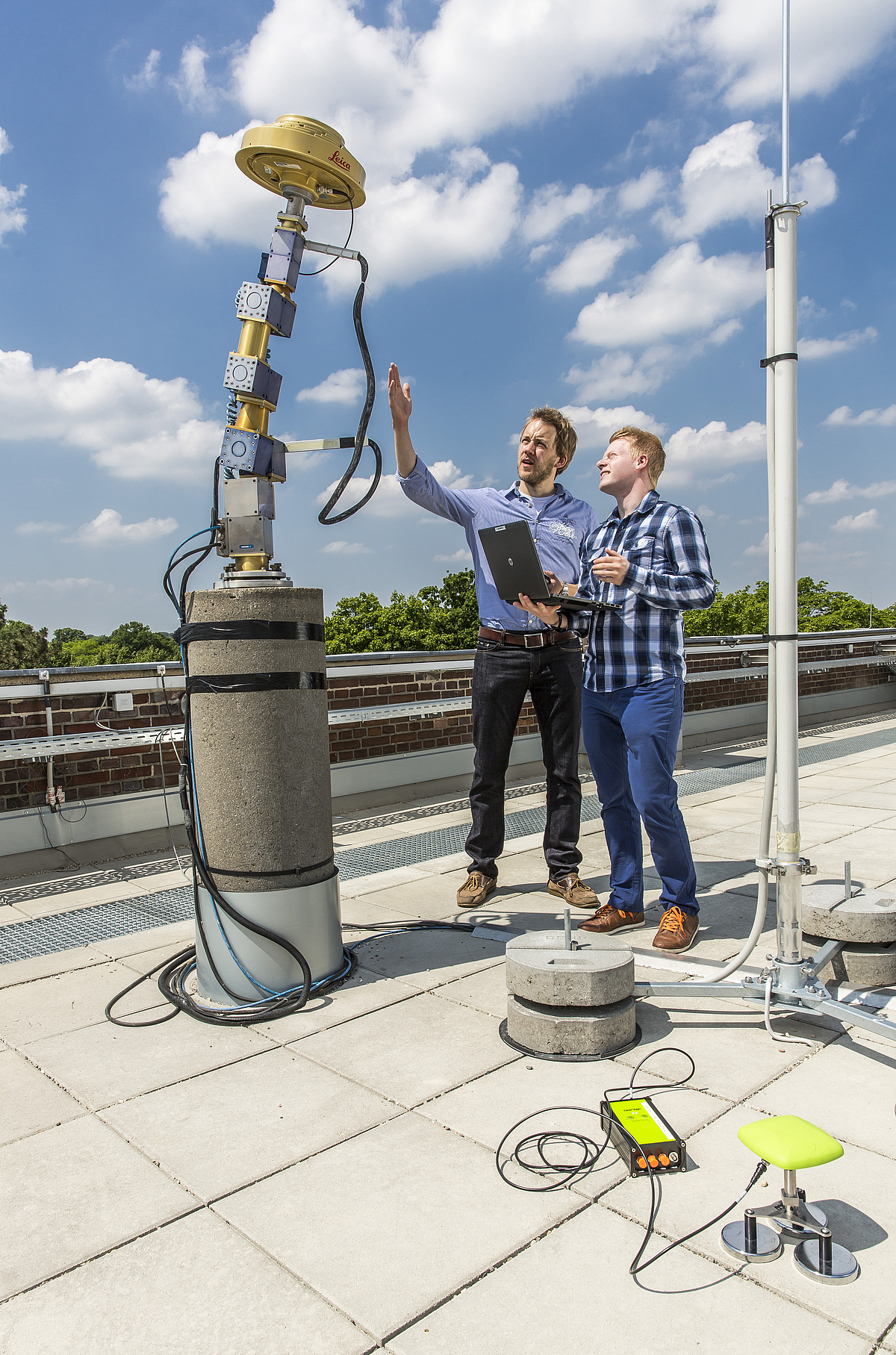



The development of the absolute field calibration of GNSS antennae (Hannover principle) was funded by the Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) in a project "Entwicklung und Erprobung eines Verfahrens zur hochpräzisen Kalibrierung von GPS-Antennenaufstellungen". This method was developed in cooperation with Geo++ (Gesellschaft für satellitengestützte und navigatorische Technologien mbH).
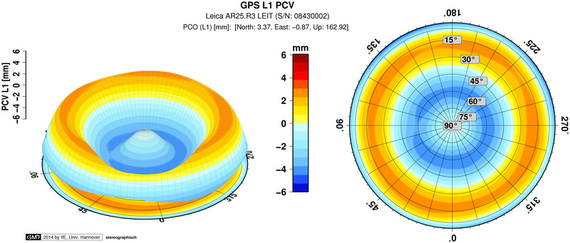
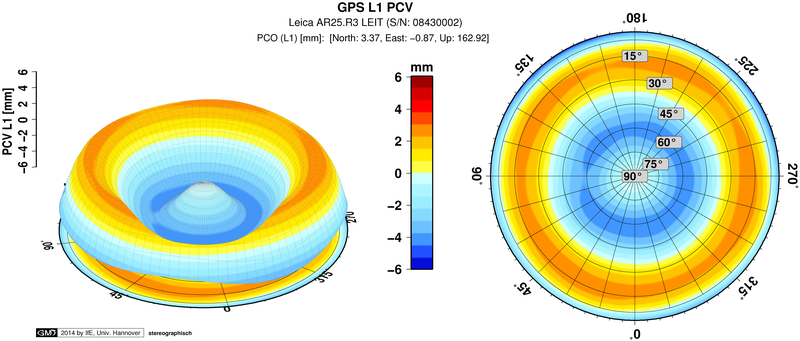
It is distinguished by a real time calibration process with a robotic arm to determine azimuth- and elevation-dependent phase center variations (PCC, PCV) of GNSS antennae with sub millimeter precision.
- Examination and analysis of GNSS reference and rover systems
- Calibration and analysis of conventional GNSS receiver antennae
- Calibration of special scientific GNSS sensors for satellite missions
- Analysis of the antenna's near field effect on directionality
- Advice and support for GNSS sensor technology
Services offered include analysis and evaluation as well as advice and support for general and specific questions about GNSS sensor technology.
Please note that due to scientific tasks to be carried out waiting times might be expected at the calibration station. Furthermore calibration can only be carried out from March to October for weather-related reasons.
A GNSS calibration for receiver antennae is available for systems GPS and GLONASS for frequencies L1 and L2.
Calibration data are delivered in the international formats (antenna exchange format - ATX). The data are valid for the upper hemisphere (0°-90°) of the antenna as well as for all azimuth ranges and refer to the antenna reference point (ARP).

 ©
IfE / T. Kersten
©
IfE / T. Kersten
Contact
 © Tobias Kersten
© Tobias Kersten
30167 Hannover

 © Tobias Kersten
© Tobias Kersten




